According to Internet Live Stats, there are over 1.7 million websites on the internet, with 4.5 billion people contributing to online interactions each day. This means your one website is fighting tons of sites to appear on the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) for a piece of 4.5 billion people. The best way has always been to use SEO and pull traffic to your site. While there are tons of paid SEO software online to help you do that, Google Search Console remains one of the best ways to do it, free or paid.
Before we get into details and find out why Google Search Console is so vital for your SEO, let’s first understand exactly what it is and how to get started.
What Is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool from Google that helps you understand how you are performing on Google Search. Once you have this information, you can easily decide what you need to do to improve your appearance on search results and bring relevant traffic to your site. You can also use Google Search Console to find and fix technical issues on your website, see who is linking back to your site, and tell if your site is mobile-friendly or not. Finally, Google Search Console is a prerequisite for your website to be featured in the Google Knowledge Panel.
Google’s search tools work hard to understand the content on your page. This is through the analysis of structured data found on the web. They label individual elements on the page allowing users to search for content on your page more specifically. For instance, structured data examples you might find on a recipe page include the recipe title, its author, how many people you can serve, cook time, calorie count and more. These information can then be used to enable special search result aspects and boosters. With the right structured data, a recipe website can appear in the graphical section of the SERP, allowing it to get a higher CTR.
What Is the Difference between Google Search Console and Google Analytics?
The main difference between the two tools is the purpose they serve. Google Search Console focuses on getting you data that helps you improve your site visibility and presence in SERPs. Thus, the tool is search-engine focused.
On the other hand, Google Analytics focuses on getting you data about your visitors and how they interacted with your website. Because you need both metrics to create a website that readers love, use both to complement each other.
Since we are covering GSC today, let’s get started on what this tool can do for your SEO needs.
How to Set Up Google Search Console?
Before you use Google Search Console, you must activate your account and link it to Google analytics and any SEO tool you use to research keywords and write content. Some tools don’t have this feature, but others like ZenBrief do.
Activate Google Search Console
Go to Google Search Console and use your business email to sign in. You will have two options. That is, domain and URL prefix, which you will use to add your website. You can use either option, so no need to pick both.
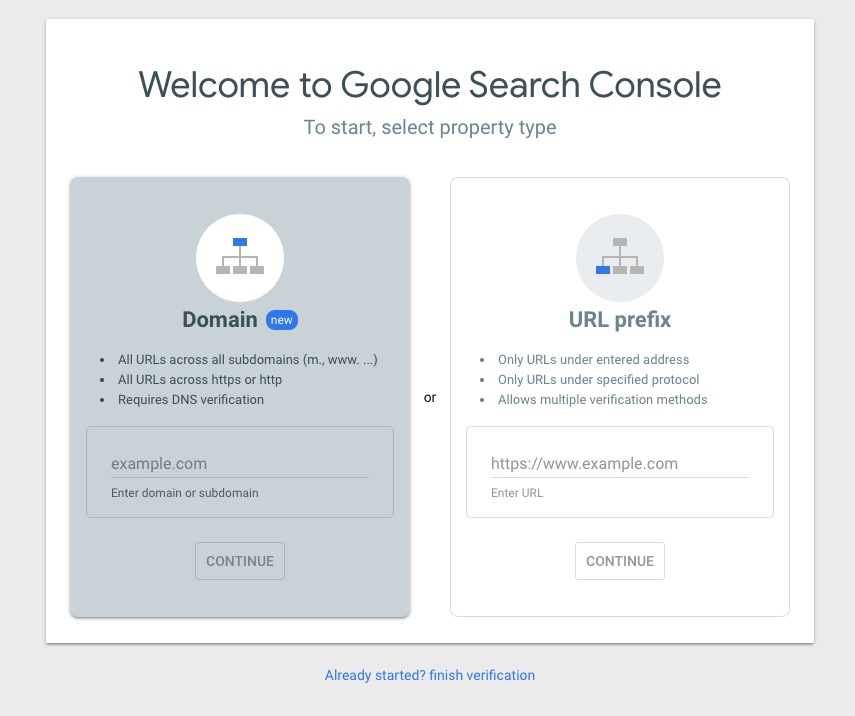
Next, you will have to verify that you own the website or property. One of the ways to do so is to rely on Google Analytics tracking ID. To find the ID, simply log in to your Google Analytics account and navigate to settings. Select property setting, basic property setting, and finally, tracking ID. Verifying your business can even simplify the verification process when you add or claim your Google Business Profile.
Set up Google Search Console permissions
Who are the owners and users of the console? This step might seem mundane but it’s important that you carefully consider who should have what permissions. Giving everyone full control can be disastrous, just as not giving them enough permissions.
The best thing with this is you can easily access Google Search Console from your admin area in Google Analytics instead of using the tools separately. To do this, go to Acquisition and select Search Console.
Submit A Site Map
A site map is a digital map that gives Google important information about your website, such as the important pages, which ones to crawl and leave out, when pages were last updated, and much more. For example, if you have a new website, submitting the URL to Search Console lets Google know that your site is ready to be crawled.
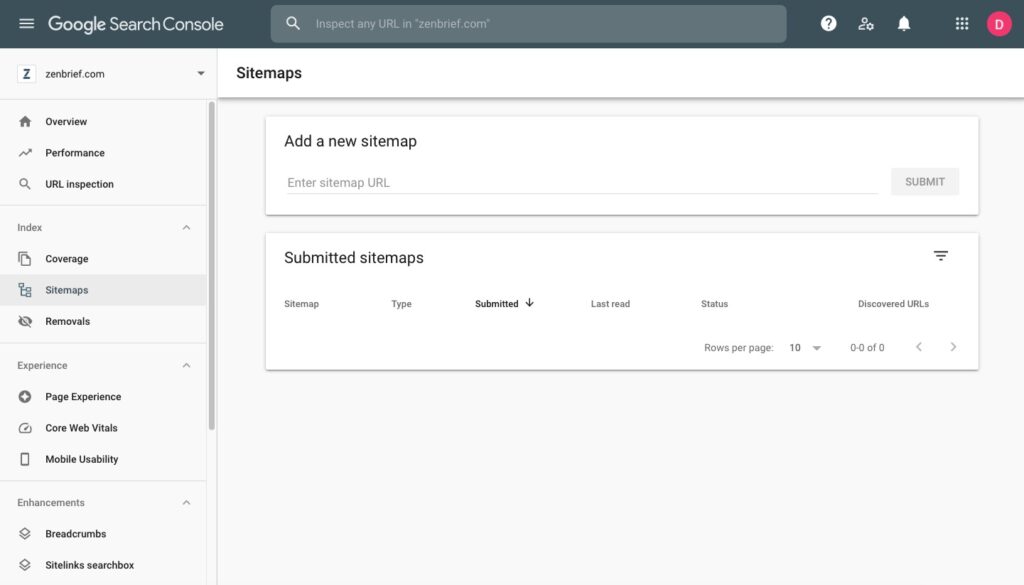
You can use a sitemap generator to create an XML sitemap and upload it to Search Console. Once you open GSC, look for “sitemap” on your left-side menu and click on it. Fill in your sitemaps URL in the appropriate space and let Search Console read your map.
You will get a report with any errors discovered so you can work on fixing the issues. Keep checking your sitemap to see if new URLs have been discovered. The good thing is, you don’t need to submit your sitemap whenever you make changes to your site.
However, if you make any major changes such as fixing errors, adding important pages or redesigning your website, it’s always a good idea to submit a new sitemap.
Understanding Google Search Console Basics
Now that you are all set, you must understand some Google Search Console basics. Like other tools, Google Search Console has a few important features you can’t ignore. For SEO reports, you will use GSC’s primary sections. These are Performance, Coverage, Experience, and Enhancement.
Performance
Under performance, you will have the search results that give you 16-months worth of data. You can filter the results so you can easily search for job posting, rich results, AMP pages, news, and non-rich AMP results.
The data found here will inform your digital strategy. The information you receive will include:
- How many impressions your website received, or how many times searches see your website when they enter a search query.
- How many clicks your site received, or how many times searchers click on your site once they land on it in the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
- The top queries searchers use to discover your website or your website’s average position in SERPs.
You will not always be interested in all the performance reports and the strategic data they offer. To help you focus on what you need, GSC has filters you can use. For instance, you can use the filter bar to select information based on the search type, data range, page, query, search appearance, and country.
In other words, you can check which country most finds your site, the device searchers use when they land on your webpage, and how Google is serving your pages.
Coverage
The coverage report shows you how your site is fairing within Google’s index. The coverage report is best used to troubleshoot technical SEO issues that often keep your pages from showing up in search results. Usually, Google sends out an email whenever there is an issue with your site, but it’s always good to keep checking to make sure everything is fine.
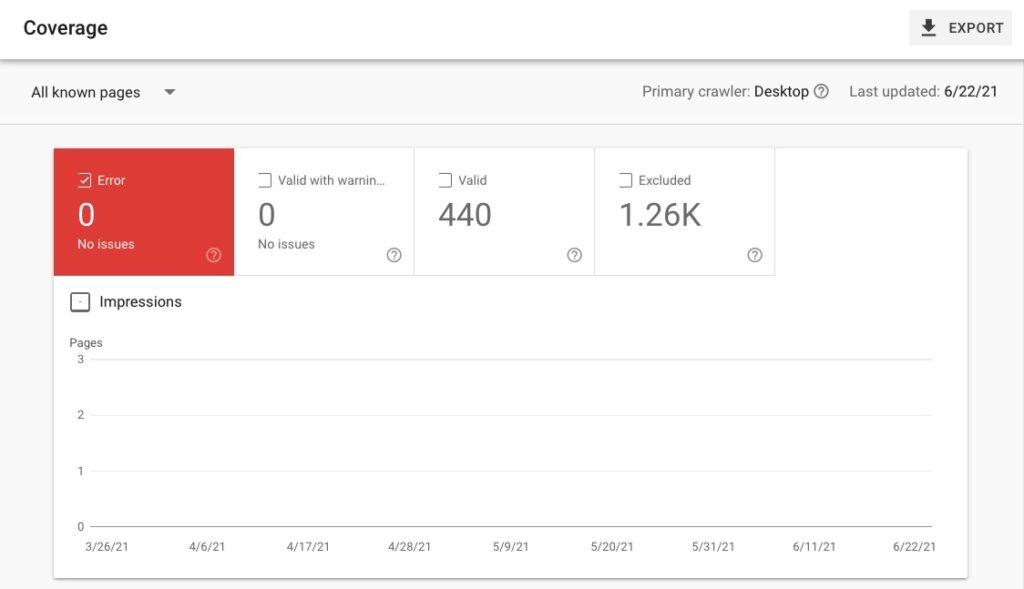
The coverage report has four options for you to look at.
- Error – this means a page is not indexed by Google and won’t appear in search results. Click on a particular error to see which page is affected.
- Valid with warning – the pages are indexed, but they don’t necessarily show up on search results. This happens when Google thinks there is a problem with the pages, and you need to be aware of it.
- Valid – the pages are indexed by Google and show up in SERPs. You only need to take action if you don’t want a particular page showing up in search results.
- Excluded – these pages are not indexed by Google and will not appear in search results. When this happens, the page may have a no-index directive or a canonical tag.
When you create new content, you should see your number of indexed pages increasing. Conversely, if you remove some pages because they no longer serve any purpose, then the number of indexed pages will reduce.
So, you know there is a problem when you notice a sudden dip in the number of indexed pages. The drop indicates that something is preventing Google from indexing the pages.
Page Experience
A while back, Google introduced a page experience update and added this report to Google Search Console. This report is a combination of the core web vitals. That is:
- Largest contentful paint, a metric measuring how fast your page loads. A good page should load in less than 2.5 seconds.
- Cumulative layout shift, which deals with visual stability. It should be less than 0.01.
- First input delay, that’s used to measure user interaction with your page. Aim for lower than 100 milliseconds.
These vitals all contribute to a good user experience. The page experience result shows you:
- The percentage of Good URLs – your core web vitals are good, and there are no mobile usability issues.
- The number of impressions you get with the good URLs
- The number of failing URLs which are usually marked as poor or need improvement.
- Any security issues your site may have which makes a good user experience impossible
- The pages that use HTTP instead of HTTPS
Many people often downplay the user experience, but you should pay close attention to it. When you and your competitor have good content, Google uses the next metric to decide who gets better ranking. If your user experience is better, you will rank higher than your competition, so take this report seriously.
How to Use Google Search Console for On-Site SEO?
On-site SEO refers to things you do on your website that impact how your site ranks. On-page SEO includes content optimization, URL structure, meta description, title tags, image optimization and more. It also includes internal links and their structure and your website design.
There is no better way to determine if your content strategy efforts are working than looking at the Search Console. So, now that you know all about the basics of Google Search Console let’s dive into how you can use it for SEO.
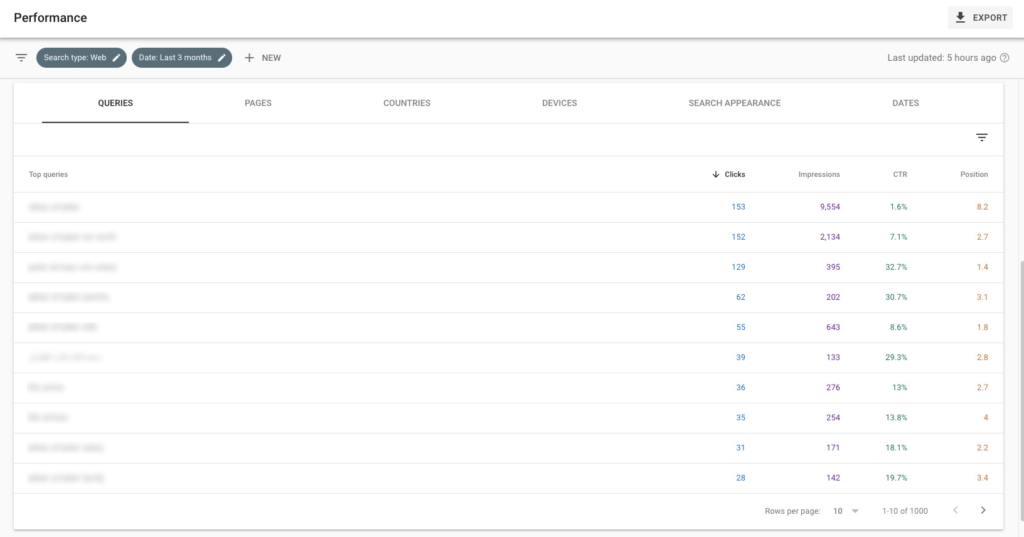
1. Find out the keywords you are ranking for
You can find this information when you look at your site’s performance. Specifically, check for “queries” within the tool. Once you click on performance, scroll to the bottom of the page to find the queries tab.
Queries show you the number of keywords your site shows up for in search results, the number of impressions the keywords attracted, and the number of times a searcher clicked on your website. Note that some impressions and clicks may come from People Also Ask (PAA) questions when the user clicks on a question, expands it, and sees your website’s answer to the question.
Right next to ‘queries’ you will see a tab for “pages.” This tab helps you see what keywords a specific page ranked for. Once you click on the desired page, click on queries to see the keywords that that specific page shows up for in search.
You can also check which country the searcher is from and the device they used to access your site. The tabs for these are next to “pages” on the menu.
To make the most of it, you should use Google Search Console together with a content optimization software. Then, using the data you collect from both tools, you will easily determine what needs to improve so you can rank higher on Google SERPs. ZenBrief makes it really easy as it comes with a Google Search Console integration in all plans.
For instance, let’s assume the keyword “best acoustic guitars” is getting tons of traffic, but it’s not performing well in the SERPs.
Through the integration of Google Search Console in ZenBrief, you can easily see what needs to be done for you to get more organic traffic from Google. Your website already ranks for queries that show up on Google Search Console. For each of those queries, ZenBrief gives you a Content Score and a Word Count, and compares it to your competition. It also provides the number of internal link opportunities that you may have missed.
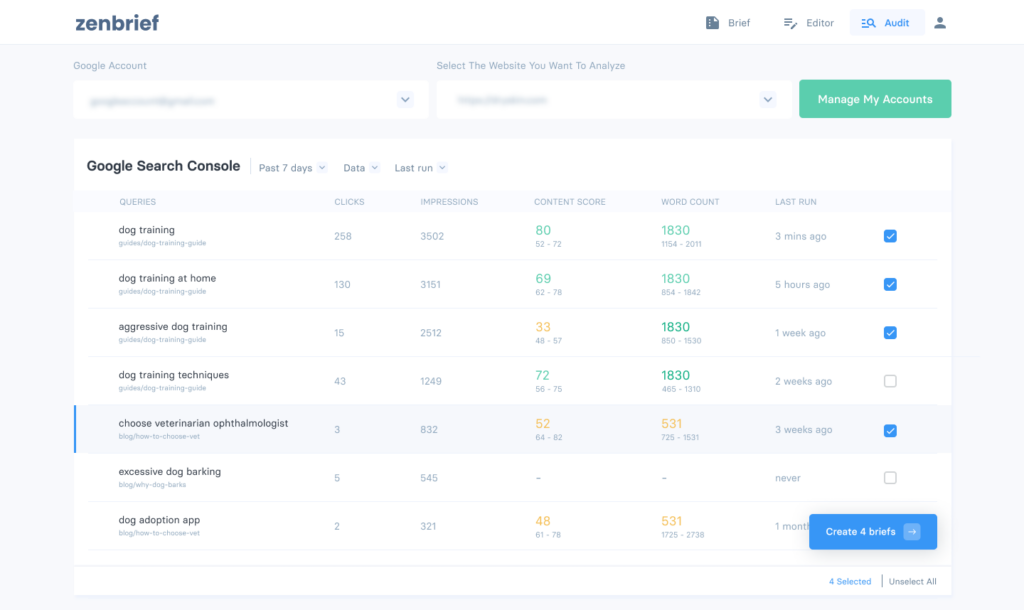
For example, if you see that your Content Score is lower than the recommended one, you know that you have to improve the quality of your content to rank higher. ZenBrief will tell you which other keywords your competition is using, which sections your competitors cover that you haven’t included and whether you should increase the number of words.
2. Improve your ranking for certain keywords
For each keyword, Google Search Console tells you your position on search results pages. This data is beneficial because you see where you rank, and thus, monitor how your ranking changes when you adjust a few things on your pages.
Let’s say your website ranks 70 for the query “best SEO tips”. Using ZenBrief’s AI content optimization together with Google Search Console information, you can improve your content’s relevance and depth for that query. Content depth, or the lack thereof, may be one of the reasons your website isn’t getting much traffic.
Once you are done with the content optimization, you can submit the site for indexing by using the inspection tool – we’ll talk about this later on in this article. After a few days or weeks, you will see your site’s new position on Google Search Console and receive data that will help you determine what else you can do to keep improving the ranking.
This alone can tremendously improve your position and increase your traffic and sales.
Note that the incremental benefit of improving the position of your page on search results, is not linear. For example, there’s a much higher impact in getting your site moving from position 11 to position 9, then from position 31 to position 29. This is because search results get exponentially more clicks the closer you get to page 1’s top search results.
Finally, if you want your page to get to position 0 on Google, you’d better focus your optimization efforts on pages that are already ranking within the top 10 search results.
3. Improve your SEO strategy
Most people don’t take a keen look at the country’s tab, but the information found here can help you adjust your SEO strategy. The search queries getting the most traffic will come from different countries. This means it’s possible to rank for search queries in a country that doesn’t help increase your sales.
Let’s go back to our earlier example of “best acoustic guitars”. If your target market is in the US and Canada, getting traffic from India may not help you sell acoustic guitars in your designated country. However, by paying close attention to the countries in your SERPs, you can adjust your future SEO strategy to focus on the countries you want. This way, you not only see an increase in traffic but also in inquiries and sales.
4. Focus your efforts on keywords you’re already ranking for
You probably used a keyword research tool to find low-hanging keywords for your website content. When you start receiving traffic from Google, use the data in Google Search Console to see which keywords you are already ranking for. If you’ve correctly optimized your site’s content, there should be a lot of overlap between the keywords you were targeting and the keywords that your site is ranking for. You may also discover new keywords that you didn’t plan to rank for. This gives you insights into people’s search intent and allows you to find topics for evergreen content.
If you have no clue about topics to cover next, this insight can also prove useful in generating fresh content ideas for new articles.
Using ZenBrief, you can now improve your content for all queries that show up in Google Search Console, and put less effort into the list of keywords you initially started with. Once you have improved your site’s ranking and clicks for those keywords, you may go back to your list of keywords and create content that helps you rank for keywords that don’t show up in Google Search Console.
5. Improve your CTR
Optimizing your Click-Through Rate (CTR) and dramatically improving your organic traffic. For instance you can scan your keywords and differentiate them from what’s common to reduce competition. This way you get more clicks instead of sharing them with a hundred other pages. Similarly you can use creative descriptive titles, better descriptions, structured data and improve your other low performing pages.
How to Use Google Search Console for Off-Site SEO?
1. See what sites link back to your site
Backlinks are valuable for SEO because they give your site a “vote of confidence” in Google’s eyes. In simpler terms, backlinks tell Google that other sites trust you, and so should Google. Through Search Console you can see who links back to you, what pages have backlinks, and what pages receive the lion’s share.
Check the domain these links are coming from and how much traffic they are sending to your site. Then, research their SERP position and look for other sites with the same strength and amount of traffic. These are great places to pitch guest posts or ask to be included in their resource page.
2. Send new pages for inspection using the URL Inspection Tool
Google usually takes a few days to notice changes on your website. For instance, if you add a new blog post, it will take Google some days before seeing any changes in Search Console because Google doesn’t know your content exists.

That’s where the URL inspection tool comes to help. The URL Inspection tool enables you to see how Google renders your site. It also sends a signal to Google so it can crawl the page, index it, and you can start receiving organic traffic sooner.
To use this tool, add your URL to the top search bar in GSC, then leave Google to do the rest. You will receive a simple report telling you that you have submitted the page for indexing. Always send your pages for indexing when you have a new post, page, or after making updates to older content.
3. Measure your site’s mobile performance
Google started using mobile-first to rank websites in July 2019 because they know how vital mobile is in driving organic traffic. According to Statista, mobile, excluding tablets, accounts for half of the web users worldwide.
With such staggering numbers, it makes sense for Google to use the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking purposes instead of using the desktop version.
So, on Search Console, click on mobile usability to check your website’s mobile performance and see how many mobile users your site gets. If you have any mobile usability issues, you have the opportunity to troubleshoot any design and development issues.
Terrible mobile experience leads to a high bounce rate, low traffic, and no customers. The most common mobile useability issues include:
- The content is wider than the screen. Fix this by ensuring your pages don’t need horizontal scrolling
- Your site’s viewport isn’t configured. Fix it by ensuring your site uses the meta viewport tag to adjust the site’s dimension based on the device used by searchers.
- Clickable elements are too close to each other, which is easily fixed by ensuring they are far apart.
One of the best ways to use Google Search Console is to pull data from it and display it using another tool. Never use the average position as KPI unless you check this keyword by keyword. Instead, focus on the pages getting high impressions, but that aren’t receiving any clicks. Use the data from Search Console and ZenBrief to determine where the problem could be and resolve it.
For instance, your content may be irrelevant depending on your title tag and meta description, or perhaps your SERPs listing isn’t captivating enough to stand out from your competition. These are essentially SEO triggers you should solve immediately to start receiving clicks.
Conclusion
Google Search Console is a great tool to analyze your search ranking. Ignoring it is bad practice for your SEO, as you are unlikely to get a more accurate tool for that purpose. Combined with a content optimization tool such as Zenbrief, Google Search Console can really strengthen your SEO efforts and help you get more organic traffic.





