Of the many SEO strategies you can use, there’s a good chance internal linking doesn’t feature in your top five. It’s not surprising; after all, there are a lot more SEO practices that can help you reach Google’s page 1 faste. On top of that, most of the articles on internal linking never fail to mention, in annoyingly great detail, how complicated the issue is.
Despite the appearance, internal linking is a very simple marketing concept and therefore should be part of your content strategy. It’s all about giving your reader more: more value, more stuff to read, and more knowledge to gain.
Sounds great, right?
What’s even better, internal linking allows you to breathe life into the old content on your site. In short, you can optimize your existing content to get more organic traffic. Rather than having numerous seemingly unrelated articles, you have a network of interconnected articles. Something your readers will truly value you for.
If you are interested in learning on-page optimization and improving your SEO ranking through internal linking, here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do it.
What Are Internal Links?
As the name suggests, internal links connect one page on your site to another. Every website has tons of pages connected this way, thanks to its design and architecture. Most sites have a simplistic overall design that includes a homepage that branches out into a menu and subpages. The design should be logical and easy to follow so both users and search engines can have an easier time finding your content.
There are different types of internal links in addition to your homepage, site menu, post feeds, and so on. The links you add within your content are referred to as contextual links. These are what users and search engines rely on to transverse all the amazing content you have on your site.
Users rely on internal links to navigate your website and find the content they want, while search engines use them to crawl your content. Internal links help define the structure of your website, and the fact of the matter is a website with a clear and well-defined structure ranks better and gets better search visibility.
If internal links really help you put your content in front of more people, why don’t more people use them?
That’s one thing those articles got right. Despite it being a simple concept, the theory, process, and best practices of internal linking and content optimization are a lot more complicated than they look. It’s both complicated and simple.
Luckily, there is a way out.
So how do you navigate this simple yet complex concept?
Well…
By learning everything there is about internal linking and how to do it right. This will present you with the best opportunity to establish and increase your rank and topical authority.
Internal Links Vs. External Links
When most people think of linking, they are most likely referring to external liking. Unlike internal links, external links are hyperlinks that connect your pages to other websites. For instance, if you write a post about car parts, you can link it to a reputable page on a different website so your reader can learn more. At first glance, external links seem counterintuitive; after all, why would you willingly send your readers to another site? You want to keep them on yours, right?
However, linking your content to trustworthy material from authoritative sites shows your reader that you know what you are writing about and that you want to offer them the best, even if it means sending them elsewhere. To search engines like Google, external linking helps you look like an authority on the matter, and it can also help search engines figure out what your content is about for SEO purposes. That said, you should also know that other websites can link back to your site too. If you publish great content on a particular subject, others might look to link their content back to you as a source for their own work.
This is where internal links come in. After users get redirected to your site, they can easily find relevant information and other important pages through the internal links you provide. Think of it this way, at school, your teacher would give you an assignment and even suggest reading a particular book to help you get the answers you need. When you go to the library, the librarian might suggest other similar books that might help you get more information on the topic you are working on.
That’s how external and internal links work. Your teacher suggesting you read a particular book is much similar to what happens when another site links to you. Once at the library (read your website), you get access to an even larger pool of information than you would get from one book. External and internal linking each has their own benefits, but you can agree both are crucial to help boost your Google ranking.
NoFollow Vs. DoFollow Links
Just as the name implies, the term no-follow link refers to a link that brings referral traffic to your page but carries very little value to a search engine. It’s used as part of an SEO strategy when a site is worried about its overuse of external links and wants to avoid being penalized by Google. It’s a normal practice that is used by high-ranking authority sites that have a lot of external links on their site.
On the other hand, do-follow links direct a search engine to follow a link to an associated site creating link juice. Therefore, when creating internal links, you want to use do-follow instead of no-follow attributes.
How Internal Links Affect SEO
Internal links matter because they help search engines find, index, and understand all the pages on your site. If used well, they can send page authority to important pages and are key for any website that wants to increase its SERP ranking.
Google’s search engine has come a long way since the early days of search engine optimization, and now it’s getting harder to game the system. You can no longer cheat your way into a high rank; you actually have to put in the work. Working on improving things such as your internal linking can drastically improve your SEO metrics, eliminating the need to game the system.
To help you understand why these links are so important, here are some of the benefits they offer.
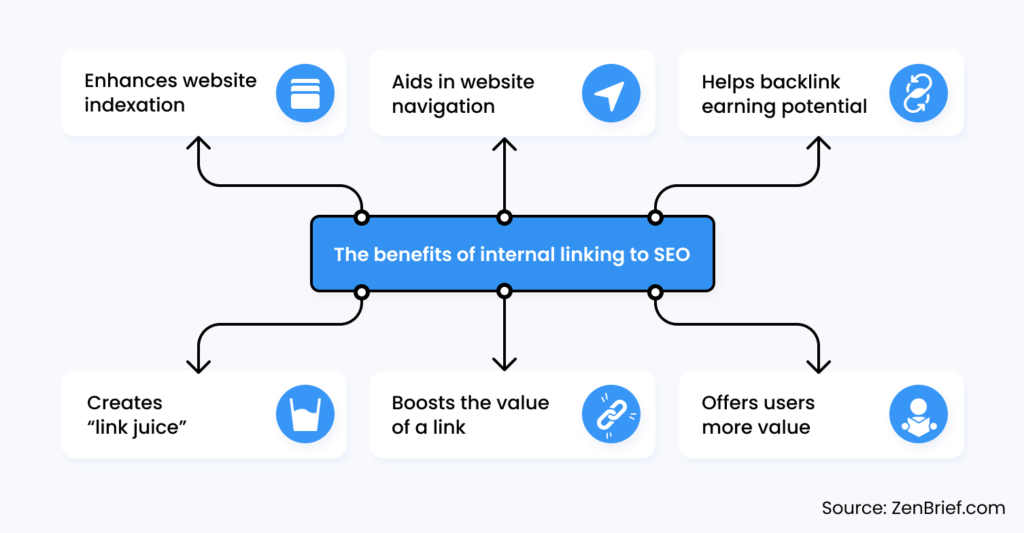
Benefits of internal linking to SEO
-
Enhances website indexation
Search engine crawlers follow link paths all over the internet to find and index websites. Think of them and large libraries, and these crawlers are trying to classify all the information in there. It would be hard to do so if they can’t tell what is on a site, right? The internal links you’ve got on your website help the crawlers to categorize and index your content. This way, when a reader searches for a particular topic or keyword relevant to your content, your work shows up. They also define the structure and hierarchy of your site.
Additionally, if you have strong internal linking, search engine crawlers have an easier time finding any new blog posts and content you publish and link. Since google’s web crawlers are always searching for new content online, if you link your work, they have fewer problems crawling and can go deeper into your site while within the available crawl budget.
-
Aids in website navigation
Google utilizes 2 kinds of bots to crawl and index pages: the fresh and deep crawl bots. The fresh bots keep an eye on the most important pages, indexing them every few days. The deep crawl bots, on the other hand, index all pages about once a month, including the most important ones. If you have a proper internal linking strategy in place, these bots have a much easier time navigating your website, and you get rewarded with improved search engine rankings.
Similarly, users have an easier time going through the content on your website. For instance, you can create a topic cluster of content relating to a target keyword. You’ll find that keywords clustering can be a powerful strategy to grow organic traffic. Alternatively, the internal links can lead them to new information about what they were searching for.
-
It improves the backlink earning potential of deep content pages
Most backlinks to your site might be to your home page, and while you might think this is a good thing, t’s not, especially for SEO. This is because while your homepage is helpful, it doesn’t contain the deep content a user might be interested in. If about 80 percent of your backlinks are linked back to your homepage, users will not keep coming back to your site. However, if this 80 percent was pointing at deep internal pages, you are offering more value to your users.
When your site is not actively publishing or promoting new content, your link profile mostly features links to conventional pages such as About us, Home, or Contact us. These, however, provide very little SEO value to your website. Creating a strong internal link structure can reverse this and boost your link juice earning potential. This is by creating clear click paths and indexation in your site so you can increase the overall crawl priority through better link distribution.
-
It spreads page authority and ranking power everywhere on your website
You may or may not have heard about link juice. It’s a bit outdated now, but it basically references a page’s authority and ranking power. Link juice can be described as the authority a page has based on the number of links pointing to it, whether internal or external. Typically the homepage on any website is king. It has most if not all of the information a user might need. So it’s safe to say it has some authority. With internal linking, some of this juice can be passed on to other pages.
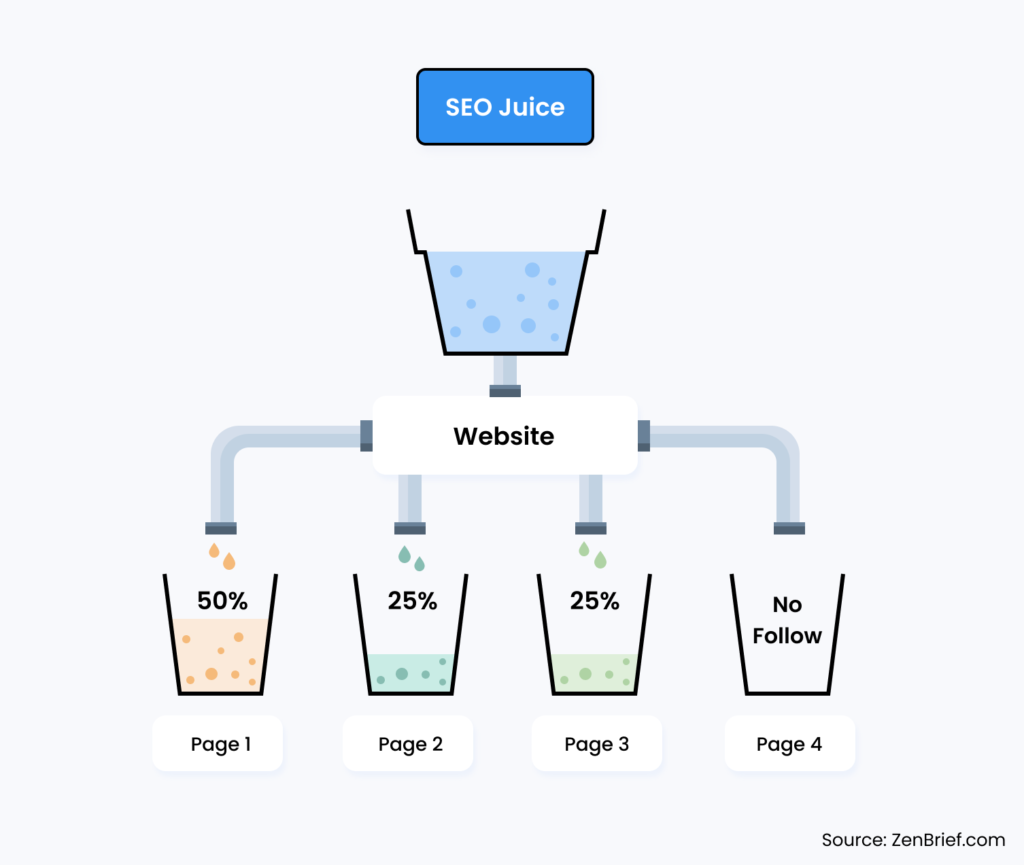
That is, if your homepage has a value of 100 percent, then theoretically, through internal links, it can usually distribute this value or linked pages. If you link about 4 pages, then each gets about 25 percent of that value. Easy.
Nevertheless, despite this concept being so simple, it doesn’t work like that. The search engine algorithm uses a far more complex system to determine value than simply relying on link juice flow. For instance, there’s a chance that two of the linked pages might get a 50 percent value meaning the other 2 will be left with nothing, or you could lose the value through a nofollow tag.
That said, if your website is well structured and indexed, you have a higher chance of getting a high SERP rank and not relying solely on link juice.
-
Internal links with anchor texts enhance link value
Internal links are simply a string of HTML that links one page to another. When created with an anchor text as opposed to an image or navigational text, its value goes up. Anchor text boosts the value of a link by adding keywords and content to the linking process. So now, rather than having a simple tag, you get anchor texts that are part of that link. This goes well with the switch to using anchor texts that flows naturally into the overall text rather than stuffing keywords into anchor texts.
-
Offers users more value
This might probably be the most relevant reason why you should use internal links. Aside from being an SEO technique, its real merit lies in the value it offers users. When most users are researching a topic, they often like to explore other pages with content that reinforces what they are reading. If users enjoy your content, then they will spend more time going through the other articles you have.
Taking time to add internal links ups the value of every post because readers can access additional resources on your website. As an added bonus, it helps keep readers on your site for longer, increasing their trust in you and generating organic traffic.
Now that you know more about internal linking, let’s take a look at topical authority and how internal linking can help.
What Is Topical Authority?
Simply put, topical authority is the perceived authority one has over a niche or an idea set rather than being an authority over a singular idea or niche. This fairly new concept suggests that Google’s search algorithm ranks websites whose content is valuable and related to the topic better than those who don’t.
For instance, you might have a wonderful page on blue cars on a site that caters to everything blue. At the same time, someone else has a page of similar quality but on a website about cars of all kinds.
Assuming that you are trying to sell cars and not blue colored items;
The website dedicated to all things blue might have a great page on blue cars, but they don’t have topical authority on them. What they have is a singular page that answers some questions about cars. However, there is nothing to signal to Google or other users that they have a breadth of knowledge on the car. Additionally, users will not get additional information on cars or answers to any related questions they might have.
The website on cars, on the other hand, does topical domain authority on cars. So it’s basically a one-stop-shop on all things cars, whether they are blue, green, red, or black.
The main idea behind topical authority is promoting reliable and helpful information that’s valuable to users, and that’s also easily accessible on a particular site or blog. It’s basically being knowledgeable in different niches. It involves having a broad and deep understanding of a topic and mastering all concepts related to it. This way, you can produce content that is coherent and valuable to readers.
Recent technological advances such as artificial intelligence have helped popularize this concept. Thanks to machine learning, search engine algorithms are now able to recognize texts and match them to relevant topics. This means that they pay less and less attention to keywords and choose to focus on shared knowledge, expertise, and topicality.
So Why Should You Care about Topical Authority?
Aside from being one of the strongest trends in SEO right now, it can provide you with a broader span of keywords and help you generate large amounts of quality content on a specific topic. On top of all that, whenever users are searching for places to reference or link, you will be it; when users are looking for answers to supplemental questions they may have – you will be it; when search engines are looking for answers to any question, you will be it; and if they are looking to determine sites that have additional information that meets other user intent, you’ve got that covered too. Your site may also be picked by Google algorithms to appear in the People Also Box, or in Google’s SERP featured snippets, which would give your site a significant boost in traffic.
As you can see, developing topical authority places you ahead of the pack.
So how does this tie into internal linking?
Internal links help create content clusters that both users and search engine algorithms identify as helpful information rather than just singular instances. These clusters offer readers more value and raise your topical trust flow and authority on the said subject.
When Internal Links Become Powerful
Now that you understand the relationship between topical authority and internal links, the next step is finding relevant link opportunities.
Linking to authoritative external sites shows search engines that your website is of high quality. You want or achieve the same thing using internal links.
So how do you achieve this?
By understanding what power internal links have. Three main areas influence internal link power, namely click taxonomy, URL structure and click depth:
Taxonomy consists of 3 parts, governance, logistics, and keywords. Search algorithms don’t care a lot about the first two; what’s important are the keywords you use to describe your content. So using the right keywords is key when it comes or your internal link structure.
URL structure covers no-follows and canonicals that help control crawling on your site.
Click depth refers to the depth a link is from the previous one. That is, from the anchor text, how many links in or out is the current page you are in.
Additionally, anchor texts also take users back to the keywords. So if you have a navigation structure that uses the wrong keywords, your anchor text will also probably use the wrong keywords.
How to Find Internal Links Opportunities
When developing an internal linking strategy, you want to craft proper paths that direct crawlers bots towards important pages.
Start by finding a strong anchor text.
Anchor text is a vital part of linking. You need to ensure that the text you use to link to your target page is relevant; this is where keyword ranking comes into play.
Next, identify the pages you want the links to point to.
You can apply a web crawler to help you find pages that have terms that match your keywords or anchor texts you chose. This web crawler will go through the source code of every page on your site, including the pillar page and find phrases in the code, and group them together. You can choose to crawl sections of your site that you believe will yield better results. However, a full site crawl will yield better results.
But, because you don’t always have the time to do this, use content creation software like Zenbrief which automatically shows you the most relevant internal links to the main topic, along with other AI-powered content optimization guidelines. This makes it easy for you and your team of content writers since you already know the keywords to use and the pages to link to.
Once the list of pages is complete, the next step is creating the link. Review the list of pages you have and select the pages to link to. Look for an opportunity in the context of the pages you chose and insert a contextual link to the page. Be sure to make this link as useful and as natural as possible, so you don’t damage the original flow of the content.
Luckily, Zenbrief helps you identify the most relevant anchor texts to use so you don’t have to crack your brain every time you need an anchor text. Further, the software also arranges the anchor text from the most relevant to the least relevant, keeping in mind your topic. And for each anchor text, ZenBrief gives you a list of the suggestions of internal links, also ranked by relevance. How cool is that?
Lastly, once the links are added, simply wait for the Google bots to recrawl the pages again and notice the new links sooner. If you want to move faster, request a crawl from Google by submitting a new sitemap through Google Search Console. Speaking of which you should also consult our guide to use Google Search Console for SEO.
What Are The Different Types of Anchor Texts?
Anchor texts are clickable texts. If you think of the world wide web as a highway, anchor texts are like signal exit signs. They send signals to website users and search engines. When used correctly, they connect you to a different lane by letting you source credible information from another site. They also help users navigate your website.
In 2012 Google introduced the Penguin algorithm. This program started using backlinks and anchor texts to determine the topic relevance of a site and to see if sites were over-optimized. In such a case, Google penalized sites with low-quality links and over-optimized anchor texts. This catapulted the role anchor texts had and magnified their importance.
In 2016, Google rolled out a Penguin update that sought to penalize anchor text offenses in real-time. This means that rather than penalizing the whole site like before, they only fault the page, but this can still affect your website’s overall traffic which will affect your revenue in the long run.
So now you know how important anchor texts are, here are the different ways you can create anchor texts the right way.
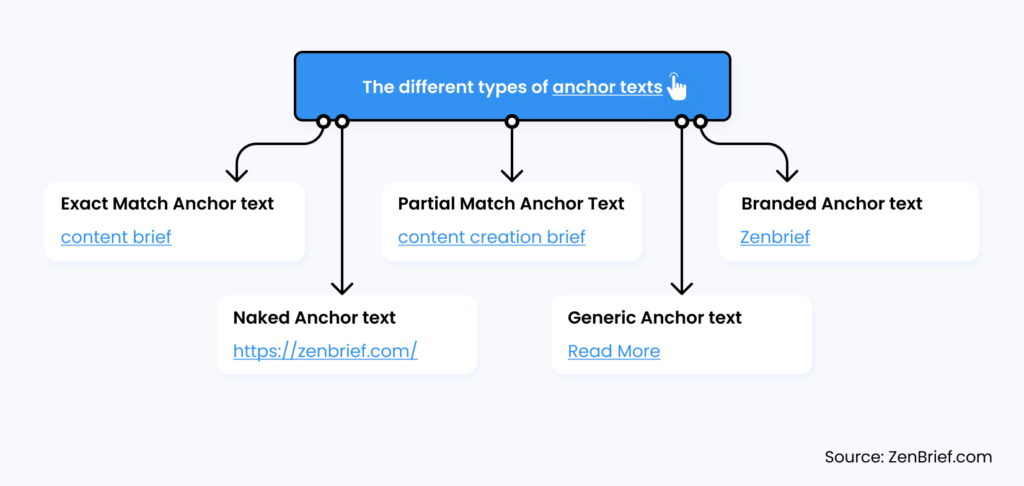
Exact Match Anchor Texts
First, you should know the various types of anchor texts available. The first being exact match anchor texts. These are anchor texts that utilize the same words as the targeted keywords for your page for instance ‘yellow car’. In the initial days of SEO, exact match anchor texts were a sure way to get your post to do well; however, since the introduction of the Penguin algorithm, Google started penalizing keyword overuse. Partial match texts, which we’ll discuss next, are a good way of still making use of these keywords without coming across as spammy.
Partial Match Anchor Text
A partial anchor text basically means that you are using a variation of the keyword describing the linked page’s topic. For instance, a partial match anchor text could be something like “every content creator should know the importance of having a detailed content brief”– if the page you are linking to covers this topic. Using partial match texts allows you to avoid overusing an exact match anchor text. To use the same example as in the previous paragraph, instead of using ‘yellow car’ as an anchor text, you would use ‘a yellow branded car’.
Branded Anchor Texts
Alternatively, if you have branded anchor texts, you can use them to establish authority such as ‘Google AdsGoogle ad words’. For outbound links, this is a great strategy and builds a strong anchor profile. It also shows search engines that you are pointing to high-quality tools and services.
Naked Anchor Texts
Next up are naked anchor texts, which are basically just the website name such as ‘https://zenbrief.com/’. These kinds of anchor texts are often deemed unhelpful, off-putting, and disruptive. It can even ultimately lead users off your page. These anchor texts might also make you seem less technically inclined than you should be. Remember to them you are an authority, so this undermines that.
Generic Anchor Text
A generic anchor text is usually a common phrase that doesn’t necessarily have anything to do with the keyword or page you are linking to. For instance, a phrase like “Read More” or “Here” is a generic anchor text.
How to Use Anchor Text Correctly?
Having understood the different types of anchor texts, here’s how to create great ones.
Stay on topic
Unfortunately, there’s a lot of misconception about what a good anchor text is. For SEO, relevancy is high on the list. That means your anchor text should be made up of words or phrases that are a close match to the topic you embed your link. For example, if you have a site about cars, if you want your users to navigate to a post you created about engine parts, you will need to add a link. For the link, you need to pick a word or phrase related to the blog’s content. Else google will flag that anchor text as manipulative and penalize your site.
Use different types of anchor texts
Using exact match anchor texts can cost you a lot since search engine filters often flag it as spam. In addition, if you only link to brand names, you might also get a similar effect. What works best is using your own varied approach. For instance, you can use a 5 percent match for exact match anchor texts, 20 percent for partial matches, 10 percent for brand name matches, and so on. However, this will vary based on what you want to achieve. For example, if you are marketing a particular brand, you can’t allocate only 10 percent.
Test and track the texts
This takes a bit of work but is a great way to test and track how they affect your SEO over time. There are various anchor text tracking tools you can use to help you achieve this. Aside from helping you test out your anchor texts, you can also view the type of anchor texts other sites are using to link back to you. With enough time and the right approach, you can build the kind of link anchor base you need to push your brand.
Knowing the different types of anchor texts and how to properly use them can help create a well-rounded internal linking strategy.
Finally, don’t forget to run a site audit from time to time. This can help you uncover broken internal links, which is a common technical SEO mistake.
How Many Internal Links Is Too Many?
When implementing your linking strategy, you don’t need too many links. In fact, Google recommends adding a reasonable number to a given page.
However, this then raises the query, what is this reasonable number?
Is it 50? 100? 200?
A lot of experts have tried to deduce what Google meant by this, but each has come up with its own number. The key is settling on a good figure depending on the length of your post. For instance, having 100 internal links might seem overkill for a 2000-word article; you are better served to have about 10 to 20. However, if you have a heavy navigation bar, you might have to reduce the number of links you add.
There’s no magical number; what you have to focus on is providing as many helpful links to the user. You want to hit a balance between building a deep site structure that’s not too flat but also give the relevant pages enough PR. As you decide the number of links to add to a page, remember you are dividing that page’s rank among the links you add. So the more you have, the minuscule the amount of page rank the linked page gets. Simply put, more links mean less PR for the linked pages; however, the same is true if you have fewer links.
But don’t go overboard. Ideally, you want to stick to the 100 link limit. However, this is just a suggestion. There are pages that have more than 100 links and are doing well, thanks to their site authority. So rather than focusing on how many links are on the page, Google is interested in the pages being recommended by that page.
Internal Linking Tips That Can Improve Your Content Marketing
Internal linking is simple; however, a lot of sites still fail at it. To help you navigate the tricky seas of internal links, here are a few helpful tips.
Start by creating a lot of great content
You can’t be seen as a topical authority on car engines if all you have on them is a few posts. You need to create more content about car engines and their various parts before you can link to them. Since content is another indispensable part of SEO, to have a killer internal linking strategy, you need to have great content to back it up. They are mutually exclusive, and one cannot exist without the other.
When you create lots of content, you get more linkable content. So a good strategy with lots of content looks more like a web rather than an organizational chart. This means pages on different levels are linked to one another.
And if you have no idea what topic to write about, check out our list of tips to find great blog ideas.
Use anchor texts
Your internal links should use anchor text instead of linked images. This doesn’t mean you can’t use images anymore: you can do so, as long as their alt-tags are correct. When creating your anchor text, remember to make use of the tips discussed earlier on how to create the anchor texts the right way.
Use deep links
The deeper you link your pages, the better. There are 2 kinds of links you should avoid using: the homepage and the contact us. As it is, most sites have too many links to their homepage. You are better served to strengthen your internal pages to boost your overall SEO rating rather than simply adding links pointing to your homepage. The same applies to contact us pages. In a mistaken attempt to get users to respond to a call to action, most sites link to their contact us pages. Don’t link to the contact page unless it is totally necessary.
Lastly, use links that are natural and relevant to the reader. Internal links must add value to the reader. In turn, this will increase user engagement. The links in your content tell search engines that the target of your link is so relevant that a user can simply jump right to it. Remember, don’t just link pages for the sake of it. You have to be intentional and connect pages that are relevant to the source text.
In Conclusion
Internal links are an indispensable part of any solid SEO strategy. It not only helps you become more valuable to your readers, but it can also help you establish your topical authority in any niche. It’s a deceptively simple concept that requires meticulous care and intentionality while executing it. When undertaken properly, you build a stronger link profile and experience better SEO.





